What was Problematic About the 1876 Presidential Election? The 1876 U.S. Presidential Election was problematic due to widespread electoral fraud and disputed results. The election led to the Compromise of 1877.
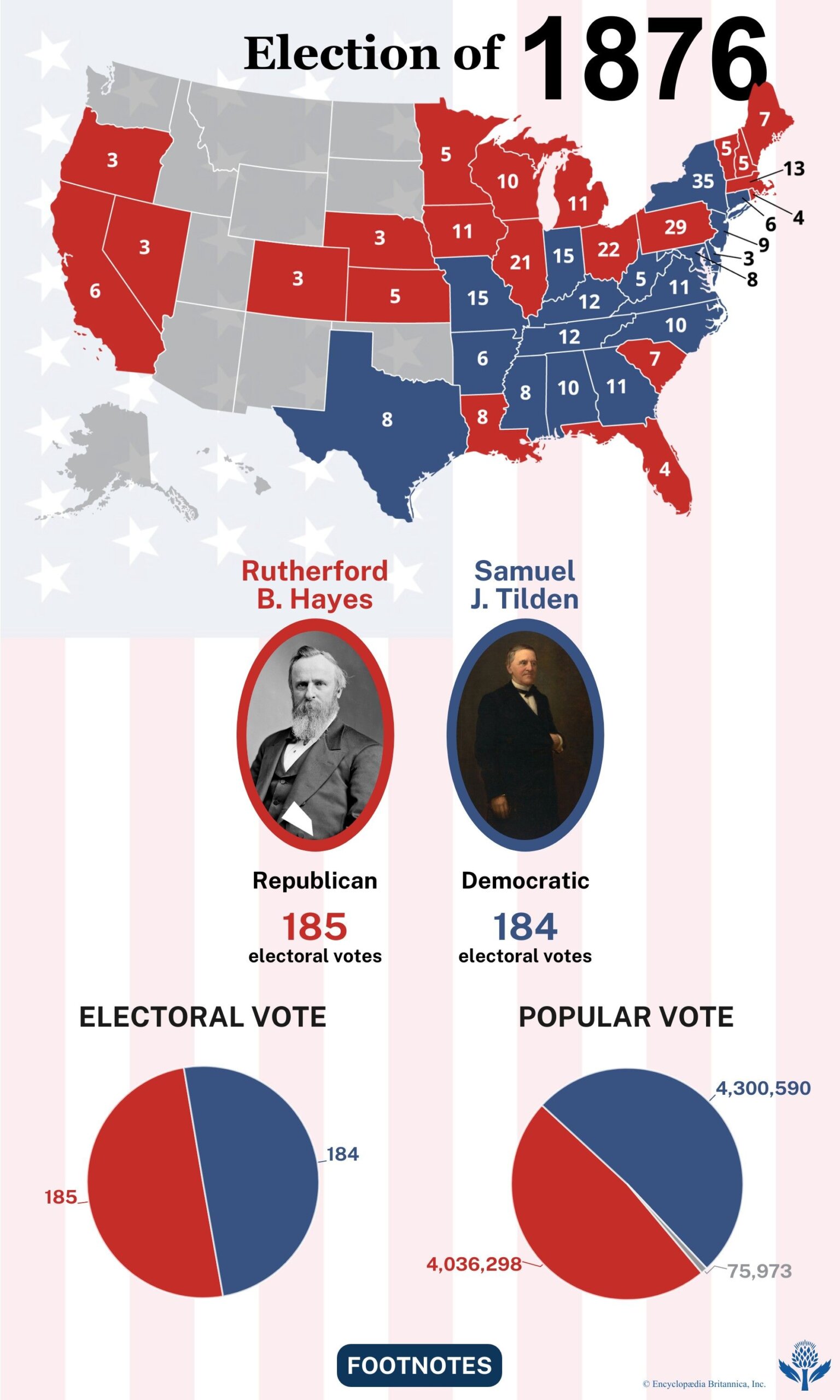
The 1876 U. S. Presidential Election between Rutherford B. Hayes and Samuel J. Tilden was one of the most controversial in American history. Both parties accused each other of fraud, voter intimidation, and ballot manipulation. Disputed results in Florida, Louisiana, and South Carolina left 20 electoral votes in question, creating a political deadlock.
The crisis was resolved by the Compromise of 1877, which awarded the presidency to Hayes in exchange for the withdrawal of federal troops from the South. This compromise effectively ended the Reconstruction era and had long-lasting impacts on American politics and race relations.

Credit: millercenter.org
Historical Context
The 1876 U. S. Presidential Election faced significant issues, including widespread voter fraud and disputed electoral votes. The contentious election resulted in an unprecedented political crisis, leading to the Compromise of 1877.
Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction Era followed the Civil War. Southern states were rebuilding. Federal troops were in the South to ensure laws were followed. There was a lot of tension between the North and South. Many people in the South were unhappy with the changes. African Americans gained rights, but many white Southerners resisted.
Political Climate
The political climate in 1876 was very tense. The country was divided. The Republican Party and the Democratic Party were in a fierce fight. Rutherford B. Hayes was the Republican candidate. Samuel J. Tilden was the Democratic candidate. The election was very close. Both sides claimed victory. This led to disputes and accusations of fraud.

Credit: theconversation.com
Candidates
The 1876 U. S. Presidential Election faced immense controversy due to disputed electoral votes. Both candidates claimed victory, leading to a Constitutional crisis. This election highlighted deep political divisions and flaws in the electoral process.
Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford B. Hayes was the Republican candidate. He was the Governor of Ohio. Many people liked him for his honesty. He promised to bring reform and end corruption. Hayes also had a strong background in law and politics. He served in the Civil War, gaining respect as a brave soldier. His supporters believed he could unite the country. His campaign focused on economic growth and civil rights.
Samuel J. Tilden
Samuel J. Tilden was the Democratic candidate. He was the Governor of New York. Tilden was known for fighting corruption. He helped to bring down the corrupt Tweed Ring in New York. Many people saw him as a reformer. His campaign promised to bring honesty and efficiency to the government. Tilden also had a background in law and business. His supporters thought he could fix the economy.
Contested States
Florida had serious issues in the 1876 election. Both parties claimed they won the state. There were reports of fraud and violence. This made it hard to know the true winner. A special commission had to decide the result.
In Louisiana, many votes were disputed. People said there was cheating and threats. Both parties sent in different results. This added to the confusion. The special commission also had to review Louisiana’s votes.
South Carolina had a similar problem. Both sides said they won. There were also claims of voter intimidation. This made the final result unclear. The special commission had to look into South Carolina’s votes too.
Electoral Commission
The Electoral Commission was created to solve disputes. It had 15 members. There were five senators, five representatives, and five Supreme Court justices. The aim was to ensure fairness. But, the commission was split. It had eight Republicans and seven Democrats. This made decisions biased.
The commission’s decisions were controversial. They awarded disputed votes to Rutherford B. Hayes. This angered many Democrats. People felt the process was unfair. The results favored Hayes. Samuel J. Tilden, his opponent, lost by one electoral vote. This caused unrest and distrust in the system.
Compromise Of 1877
The Compromise of 1877 ended the dispute. Republicans agreed to withdraw federal troops from the South. Democrats agreed to recognize Rutherford B. Hayes as President. This deal resolved the election but had serious consequences.
The removal of federal troops allowed Southern states to impose Jim Crow laws. These laws discriminated against African Americans. Voter suppression and segregation increased. The compromise led to the end of Reconstruction. This period of progress for African Americans stopped abruptly.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Public Reaction
The North and South reacted differently. The North supported Hayes. The South backed Tilden. This division was deep. It was a reminder of old conflicts. Tensions were high. People were anxious about the outcome. Some feared violence. Others hoped for a peaceful resolution. Both sides wanted their candidate to win.
Newspapers played a big role. They influenced public opinion. Some papers were biased. They took sides. This made the situation worse. People trusted their local papers. They believed what they read. This caused more division. Accurate news was hard to find. Many stories were exaggerated. This led to confusion and doubt.
Long-term Consequences
The 1876 U.S. Presidential Election led to changes in federal policies. These changes had a big impact. Federal troops were removed from the South. This marked the end of the Reconstruction era. Many Southern states passed Jim Crow laws. These laws enforced racial segregation. Civil rights were greatly affected. Voting rights for African Americans were restricted. Many people were unhappy with these changes.
The election had a lasting impact on civil rights. African Americans faced more discrimination. Their right to vote was taken away in many places. Jim Crow laws became more common. These laws created separate facilities for blacks and whites. Schools, restrooms, and public places were segregated. This unfair treatment lasted for many years. The fight for civil rights continued into the 20th century.
Lessons Learned
The 1876 election showed flaws in the electoral process. There was confusion over electoral votes. States sent in different results. This created chaos and disputes. The Electoral Commission was formed to resolve it. This was not an ideal solution. A clearer process was needed.
Political integrity was questioned in 1876. Corruption was rampant. Bribery and intimidation were used to win votes. There was a lack of trust in the system. Both parties accused each other of fraud. The public lost faith in fair elections. Stronger laws were needed to ensure honesty.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Caused Controversy In The 1876 Election?
The 1876 election was controversial due to disputed electoral votes and allegations of voter fraud and suppression.
How Was The 1876 Election Resolved?
The election was resolved by the Compromise of 1877, which awarded disputed electoral votes to Rutherford B. Hayes.
Why Is The 1876 Election Significant?
The 1876 election is significant because it marked the end of Reconstruction and highlighted electoral process flaws.
Conclusion
The 1876 U. S. Presidential Election highlighted deep flaws in the electoral process. It exposed vulnerabilities and fueled political tensions. Understanding these issues helps us appreciate the importance of fair elections. By learning from history, we can strive for a more transparent and just democratic system.

1 thought on “What was Problematic About the 1876 Presidential Election?”